Background: Rapamycin plays a protective role in kidney Ischemia Reperfusion (IR) injury in early stage, but the mechanisms involved haven’t been thoroughly revealed so far. We hypothesized this protective effect of rapamycin is relevant to the remodeling of immune microenvironment. With this purpose, we aim to investigate the change in proportion of Dendritic Cells (DCs), macrophages and Natural Killer T (NKT) cells in spleen, peripheral blood and IR induced kidney before and after rapamycin administration in a murine renal IR model. In addition, the effect of rapamycin on damage-promoting and damage-preventing cytokines in IR induced kidney was also investigated.
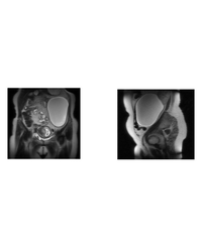
Materials and Methods: Balb/c mice were subjected to renal 30 min ischemia followed by 24h reperfusion. Rapamycin (2.5ml/kg) was administered by gavage daily, starting 1day before the operation. Renal function and histological changes were assessed. The proportion of NKT cells, macrophages and DCs in peripheral blood, spleen and kidney was detected by flow cytometry. The expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1(MCP-1), Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α), Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and anti-inflammatory cytokines Interleukin-10(IL-10), Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (TGF-β) were determined by RT-qPCR.
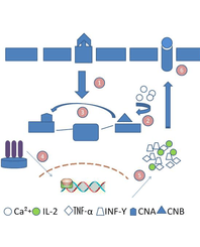
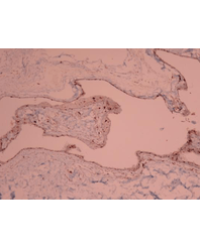
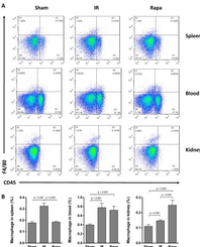
Results: Rapamycin significantly improved renal function and ameliorated histological injury and inhibit cellular apoptosis in IR-induced kidney tissue. The proportion of macrophages in spleen was decreased in rapamycin-treated group than in the sham and IR group. In contrast, the proportion of macrophages was raised in rapamycin group in comparison with the sham and IR group in the kidney. In spleen, rapamycin increased the proportion of DCs compared with the sham and IR group, but the proportion was decreased in peripheral blood and kidney. In rapamycin-treated group, the proportion of NKT cells in spleen was significantly decreased but increased in peripheral blood and kidney. In addition, rapamycin dramatically down-regulated the expression of IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α and IL-1β and up-regulated IL-10 and TGF-β compared with IR group.
Conclusion: Rapamycin may protect kidney from IR injury through remodeling immune microenvironment- -modulating the proportion of DCs macrophages and NKT cells in spleen, peripheral blood and kidney and the expression of inflammatory- related cytokines.
Chao Zhang1,2,4, Lingyan Wang3 , Yi Zhang3 , Cheng Yang1,2* and Ruiming Rong1,2,5*