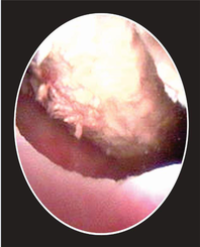
Background: Double J (DJ) ureteral stent is being used in various urological and non-urological procedures. Indications for double J ureteric stents include; negotiating the obstruction and maintaining adequate drainage from kidneys, and as an adjunctive procedure to Extra Corporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL). A forgotten DJ stent is not uncommon in developing countries and is particularly seen in patients with poor socioeconomic status. These patients present with flank pain, hematuria, irritative voiding Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS) and even lend up with features of renal failure. Management of forgotten DJ ureteral stents is not only important for patient’s perspective but also for the surgeon’s prospect due to its medico-legal implications.
Aim: To address a unique complication of forgotten DJ stent; its endourological management and preventive measures to avoid devastating complications.
Study design: Descriptive study.
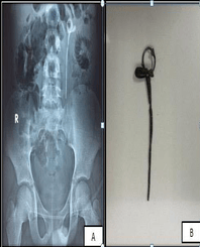
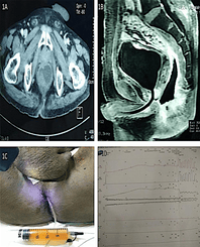
Methods: Retrospective data search from 2008-2015 revealed 47 patients admitted with forgotten ureteral stent includes (broken and encrusted) were managed endoscopically. Patients were evaluated with X-ray, ultrasonography of Kidney Ureter and Bladder Region (KUB), Intravenous Urography (IVU) and non-contrast computed tomography, renal function test (where indicated). Endourological procedure for DJ stent removal was decided according to the location of stents.
Results: A total of 47 patients (males: 34, females: 13) were included in the study. The mean age of patients was 23.53 years (range 4-65 years); mean duration of stent insertion was 39 months (4-68 months). Fifteen patients (31.9%) had stent insertion following percutaneous nephrolithotomy, 8 (16.96%) following Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy (URSL), 3 (6.3%) following pyeloplasty, 10 (21.2%) following ureterolithotomy, 6(12.72%) following pyelolithotomy and 3 (6.3%) following ureteric re-implantation. Two patients (4.2%) had DJ insertion for bilateral upper ureteric calculus with deranged renal function. PCNL was performed in 10 (21.2%), combined PCNL and CLT in 15 (31.8%), URSL in 12 (25.44%), combined URSL and CLT in 18 (38.16%), CLT alone in 11 (23.32%) cases.
Conclusion: Forgotten double J ureteral stent still a common and preventable complication in developing nations, patients may lend up in renal failure. Its removal is a challenging task.
Ankur Jhanwar1 , Ankur Bansal1*, Gaurav Prakash1 and Satyanarayan Sankhwar1