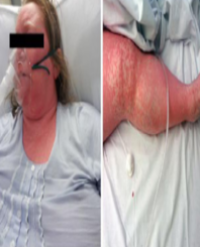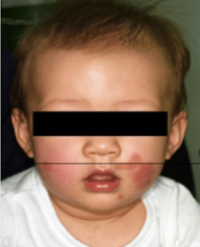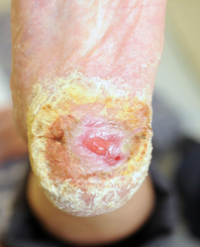
Sclerodermatous Skin: An Immunohistochemical Study
Objective: Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is primarily characterized by autoimmunity, microangiopathy, and tissue fibrosis. Hypoxia, a powerful stimulator of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), may be responsible for excessive expression of chronic VEGF in SSc. The oxygen-regulated α-subunit of HypoxiaInducible Transcription Factor-1 (HIF-1α) plays an important role in transcriptional regulation of VEGF. The protein phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is responsible for dephosphorylation of proteins and thereby promotes tissue repair.
The present study aimed to examine the expressions of HIF-1α, PTEN, and VEGF in patients with scleroderma in an attempt to estimate prognosis and guide therapeutic decisions. We therefore studied the expressions of HIF-1α, VEGF, and PTEN in skin samples exhibiting the features of scleroderma.
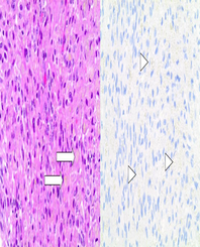
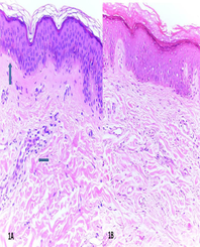
Methods: Skin biopsies of patients were obtained and samples were stained with primary antibodies following PTEN, VEGF and HIF-1α, immunohistochemically.
Results: The SSc and the control group were compared with respect to staining of epidermal keratinocytes, fibroblasts, and the endothelial cells for the antibodies. SSc patients displayed a reduced VEGF expression in endothelial cells. The lesion group showed a significantly lower staining of epidermal cells and endothelial cells for PTEN. SSc group was also characterized by a significantly weaker HIF-1α expression compared to the control group.
Conclusion: In scleroderma skin samples, manipulated expression of these molecules at varying stages of the disease may affect the prognosis of scleroderma.
Rabia Bozdogan Arpaci1*, Tuba Kara1 , Yasemin Yuyucu Karabulut1 , Didar Gursoy1 , Yalçın Polat2 , Gulhan Orekici3 and Umit Tursen4