Feasibility and Clinical Outcomes of Individualized Bone Cement Prosthetic Replacement for Advanced Lunate Bone Necrosis
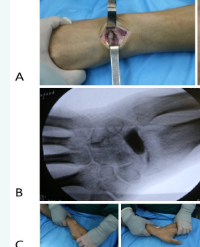
Purpose : To investigate the feasibility and clinical outcomes of individualized bone cement prosthetic replacement in treating advanced lunate bone necrosis. Methods : Nineteen patients (age > 45) diagnosed with advanced lunate bone necrosis underwent the removal of the necrotic lunate bone and replaced with an individualized bone cement prosthetic between January 2010 and December 2020. The visual analogue scale (VAS), range of motion (ROM), grip strength, MMWS (mayo modified wrist score), DASH (disability of arm, shoulder, and hand), carpal height ratio (CHR), ulnar carpal distance ratio (UDR), scaphoid translation ratio (STR), radio scaphoid angle (RSA), and the osteoarthritic were also measured to evaluate the results after at least 1year of follow-up. Results : Nineteen patients were followed up for an average of 63.21 months. At the last visit, the patient’s VAS score was (1.47 ± 0.47) points, and ROM was (130.53 ± 21.34)°, showing improvement compared to preoperative(P < 0.05), although still slightly limited compared to the unaffected side (P < 0.05); the grasp force, MMWS, and DASH scores significantly improved after surgery (P < 0.05), with no further deterioration in wrist joint function compared to postoperative results (P > 0.05). At the last visit, the CHR improved to (0.50 ± 0.06)° and the RSA to (58.8 ± 6.91)° compared to preoperative values (P < 0.05); however, the CHR was still slightly lower than the healthy side (P < 0.05). No significant changes in UDR and STR were observed after surgery (P > 0.05). Additionally, 1 case of bone cement was slightly displaced, and 3 cases showed signs of wrist joint osteoarthritis during the follow-up period. Conclusion : Individualized bone cement prosthetic treatment was effective for advanced lunate bone necrosis in middle-aged and elderly individuals. It helped restore the original anatomical structure, prevent further collapse, and enhance hand function.
Yuan-qiang Li¹ , Wan Chen¹ , Hong-Tao Li² , Xin-gang Wang² , Yu-ping Yang³* and Cheng-Song Yuan¹*