Going Down the Rabbit Hole: Functional Recovery from Alice in Wonderland Syndrome during Rehabilitation Therapy. A Case Report
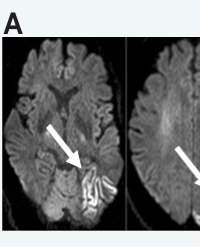
Cognitive deficits can impact functional outcomes as well as the efficacy of rehabilitation therapy after stroke, but these must be understood in the context of the specific cognitive impairments. We describe here functional improvement during admission to an inpatient rehabilitation facility (IRF) in a patient with an uncommon form of cognitive abnormality, Alice in Wonderland Syndrome (AIWS), which is characterized by visual and other perceptual distortions. The course of this syndrome in the context of inpatient rehabilitation therapy has not been previously described. A 52-year-old male with an acute ischemic infarct involving the left (dominant) occipital, posterior parietal, and posterior temporal lobes received intensive rehabilitation therapy in an IRF setting. The patient reported complete resolution of his AIWS symptoms by day 14 of his IRF admission (day 22 after stroke onset), with daily assessments showing steady gains in his self-care score. Current results suggest that intensive rehabilitation therapy can be provided in the setting of AIWS, and that functional recovery can occur in the presence of AIWS symptoms.
Ming Wu1, Shelley Schwartz2, Steven C. Cramer3*, and Michael Su3