Background: Assessment of tissue oxygenation and vascular function is an integral component in the management of chronic wounds. Current practice in wound centers is screening with Pulse Volume Recording (PVR) or Transcutaneous Oxygen Saturation (TCO2 ) to evaluate safety of compression wraps, utility for vascular intervention and expected response to Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT).
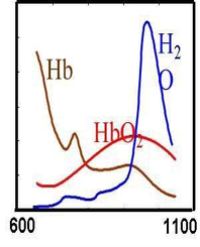
A near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy device (Kent, Calgary) using 4 wavelengths of light to determine O2 saturation of hemoglobin (Hgb) in cutaneous tissue has been developed. The low absorption of light by H2O and melanin in the NIR range allows for measurement of absorption of deoxygenated and oxygenated hemoglobin and for the calculation of O2 saturation. The purpose of this study is to determine the correlation between the gold standard TCO2 and NIR spectroscopy in measuring cutaneous O2 .
Materials and methods: 20 patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III who had measurements of TCO2 (Perimed, Stockholm) also had simultaneous measurements obtained by NIR spectroscopy. The investigation was reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board for Human Subjects at WVU. The Hemoglobin/ O2 dissociation curve at 370 degrees C, pH=7.4 and pCO2 =40 was used to calculate O2 saturations from measurement of TCO2 .
Results: Data pairs were analyzed using linear regression and the relationship y=0.93 x+5.35 with a correlation coefficient=0.92 and r2 =0.84 was calculated.
Conclusions: There was a significant correlation between measurements of tissue oxygenation using TCO2 and NIR spectroscopy. NIR spectroscopy has the advantage of not requiring skin contact and measurements can be taken even in the wound bed. Other advantages include: 1). Time (2 minutes vs. 90 minutes) and 2). Disposable cost ($150 –TCO2 vs. $0-NIR spectroscopy). 3). The ability to perform serial studies over time. Further studies are warranted to determine if this information is useful in determining response to HBOT or in predicting wound-healing trajectory
Robert E. Bowen, M.D.1*, Ginna Treadwell RN1 and Mark Goodwin RRT1