Characterization of Endophyte Microbiome Diversity in Chia Plant (Salvia hispanica L.)
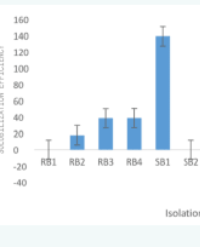
A total of 9347 fungal and bacterial endophytes were isolated from the roots, stem and leaves of chia plant. Roots harbored more number of fungal endophytes than either stem or leaves whereas stem supported more number of bacterial endophytes than either roots or leaves. The nutritious plant supported more of gram negative compared to gram positive bacterial endophytes. The most common bacteria isolated were Pseudomonas Bacillus, and Cocci. The fungal endophytes isolated from root, stem and leaves of the chia plant showed the presence of Penincillium, Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Macrophomina spps. Dominant fungal endophyte was Aspergillus spp. which was found in all the plant parts instigated. Roots of the plant possessed maximum nitrogen fixers followed by stem and leaves. A proportion of 55% for the bacterial endophytes isolated from the plant chia plant were able to fix nitrogen whereas 25% were able to solubilize phosphorous. The phosphate solubilization efficiency was found to be highest for the Aspergillus spp at 83%.
Jasira Jzar1 , Mary Simiyu2 , Joseph Mafurah2*, Joshua Ogendo2 and Anne Osano3