Right Precordial St-Segment Elevation in Patients with Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy and Primary or Secondary Ventricular Fibrillation
Background: In arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy ventricular fibrillation can be the first manifestation of the disease (primary VF). As an interaction between arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy and Brugada syndrome with regard to the so-called connexome is possible the hypothesis is that primary ventricular fibrillation belongs to Brugada syndrome and later progresses to arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.
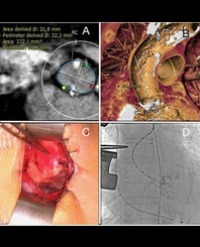
Method: A collective of 404 patients with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy were investigated to answer the question how many patients have right precordial ST-segment elevation in primary or in rare cases - secondary ventricular fibrillation.
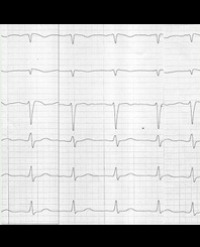
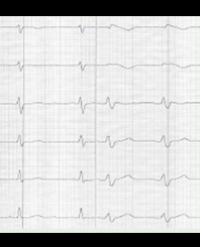
Results: 9/14 patients had primary ventricular fibrillation and 2/9 patients (15 males, mean age 43.3 ± 9.6 years) had secondary ventricular fibrillation with had non-significant (< 2mm) coved-type ST elevation, Brugada type II ECG or atypical ST elevation in right precordial leads. Ajmaline challenge was not done in any case. In this cohort of patients coved-type or atypical right precordial ST-segment elevation was statistically significant (p < 0.005) for the development of ventricular fibrillation.
Conclusion: II seems that the so-called connexome is a relevant finding to predict ventricular fibrillation as the first manifestation of the disease with insignificant coved-type or atypical right precordial ST elevation.
Stefan Peters*